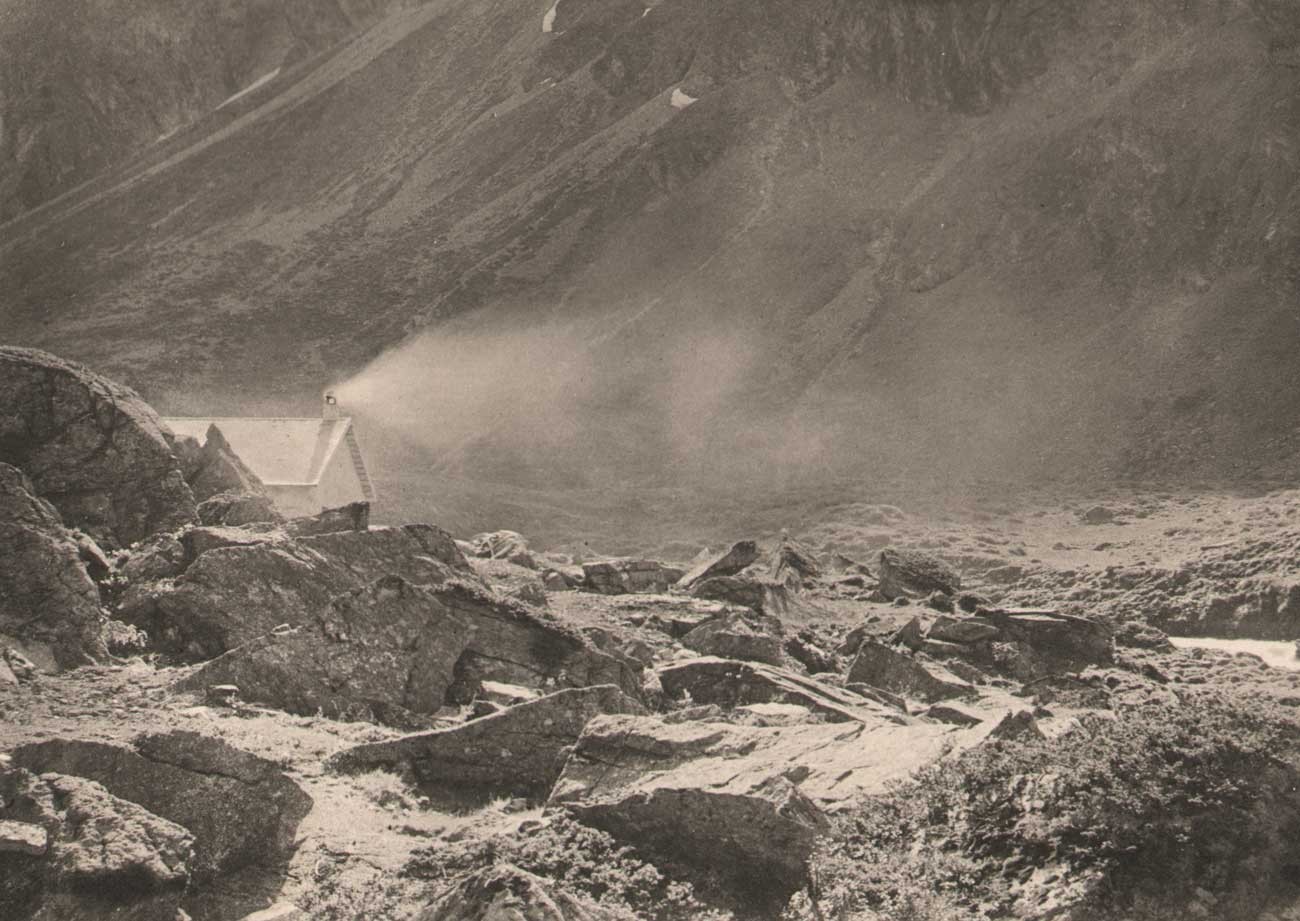
Föhn
From Wikipedia: (accessed February, 2015)
A Föhn or Foehn is a type of dry, warm, down-slope wind that occurs in the lee (downwind side) of a mountain range.
It is a rain shadow wind that results from the subsequent adiabatic warming of air that has dropped most of its moisture on windward slopes (see orographic lift). As a consequence of the different adiabatic lapse rates of moist and dry air, the air on the leeward slopes becomes warmer than equivalent elevations on the windward slopes. Föhn winds can raise temperatures by as much as 32 °C (58 °F)[1] in just a matter of minutes. Central Europe enjoys a warmer climate due to the Föhn, as moist winds off the Mediterranean Sea blow over the Alps.