A little over seven years ago, this archive finally acquired the monumental European portfolio Nach der Natur, (After Nature) published in Berlin in early 1897.

Detail: Gold-Stamped Cover title for Portfolio “Nach der Natur”. Photographische Gesellschaft in Berlin, 1897: 49.8 x 37.0 x 2.2 cm. Blue fabric cloth over boards. Translated: AFTER ◦ NATURE PHOTOGRAVURES AFTER ◦ ORIGINAL PHOTOGRAPHS ◦ BY AMATEUR PHOTOGRAPHERS PUBLISHED ◦ BY THE PHOTOGRAPHIC SOCIETY BERLIN. . With Forward by Franz Goerke & essay by Richard Stettiner. The folio consists of 32 hand-pulled photogravures: 25 individual plates and a further 7 reproduced within the letterpress. From: PhotoSeed Archive
Composed of 32 sumptuous hand-pulled photogravure plates, I learned it was considered a cornerstone to any important collection of artistic photography when first reading about it almost 25 years ago. And, as persistence can sometimes pay off, a Dresden antiquarian bookseller listed the folio, along with other titles, appearing in my inbox in March of 2017. The portfolio itself is the artistic historical record for Berlin’s 1896 International Exhibition of Amateur Photography (Internationalen Ausstellung für Amateur-Photographie) held in the Reichstag building, the German government’s legislative headquarters, which had newly opened two years prior in mid 1894.
Approximately 580 exhibitors took part from around the world, with one reviewer commenting that other than the scientific entries, in terms of mounted photographs: “there may have been several thousand of them”. The exhibition had the support of Victoria, Empress of Germany and Queen of Prussia, the first born child of Queen Victoria of Great Britain and Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha: a chip off the proverbial block per chance? It’s well known Albert had a passion for employing early photography to document the British Royal family.
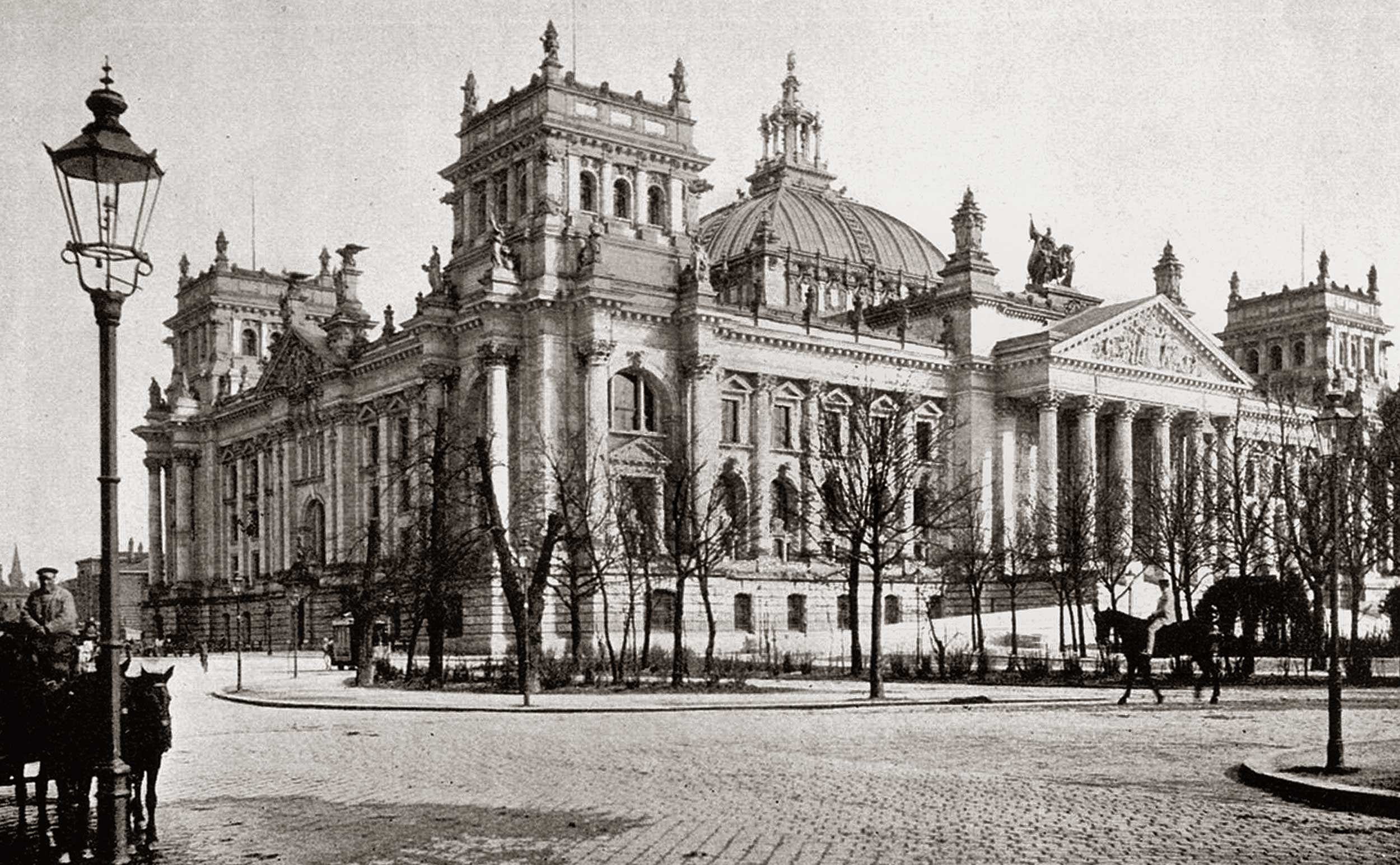

On September 3, 1896, Berlin, Germany’s Reichstag building, shown here around 1895, opened its ornate entrances on September 3, 1896 to host the International Exhibition of Amateur Photography (Internationalen Ausstellung für Amateur-Photographie). Over 580 exhibitors from around the world took part and 26,000 visitors attended the salon during the months of September and October 1896. Today the Reichstag is home to the German federal parliament, known as the Bundestag. Photo source: Grüße aus Berlin und Umgebung. Verlag Kunstanstalt W. Sommer, Berlin-Schöneberg 1898
Due to this work being an important influence on the perception of photography as art in the public discourse during the last years of the 19th century, I’ve dedicated some time in pulling contemporary reviews for the exhibition, and have further translated the entirety of the letterpress for the portfolio, along with acknowledgements, etc. from editor Franz Goerke and the main portfolio essay penned by Richard Stettiner. I will continue my thoughts at the conclusion of this post on the importance of the photogravure plates from this work and how it influenced Alfred Stieglitz in America, with the baton first taken up by Goerke- an important proponent of the photogravure process. Goerke had shown a series of mounted photogravures at the exhibition- logically continuing his favored reproduction process by assembling Nach der Natur as a remembrance of it. But first, some contemporary excerpts laying out differing perceptions of the 1896 Berlin exhibition by the German photographic press:
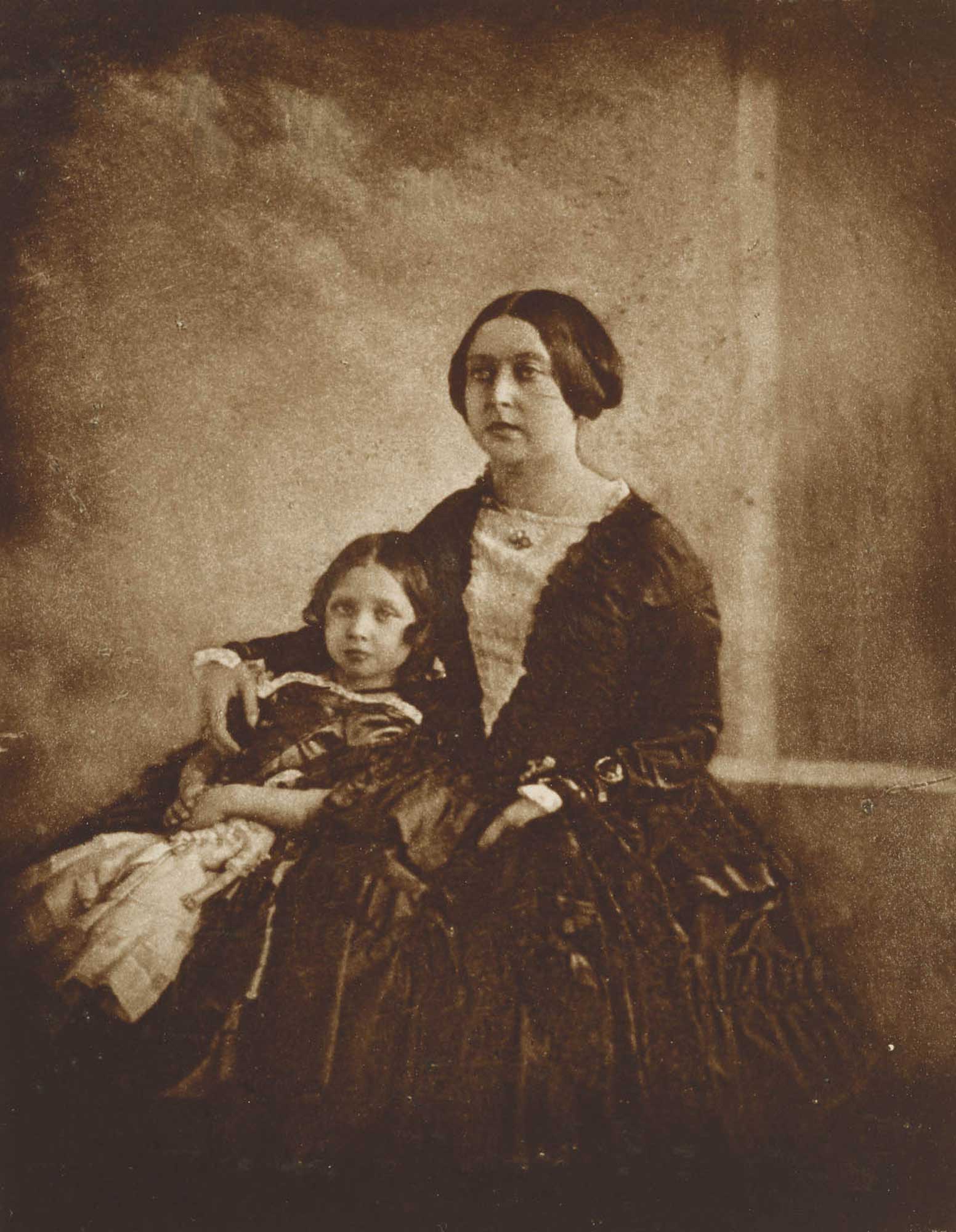
1845: The future Empress Friedrich, German Empress and Queen of Prussia (1840-1901) is shown at left seated with her mother, Queen Victoria (1819-1901) of the United Kingdom. The Empress was the official patron for the 1896 Berlin amateur photographic exhibition, with the 1897 portfolio “Nach der Natur” dedicated to her. Carbon print c.1889-91 by Hughes & Mullins from an original 1845 daguerreotype. This is probably the earliest photographic likeness of the Queen and the Princess Royal. Photograph: Royal Collection Trust: RCIN 293131
Observations: The German Photographic Press (translated)
Photographische Mitteilungen, Berlin: October, 1896: reviewer Paul Hanneke:
⎯ On September 3rd, the international exhibition for amateur photography opened in the new Reichstag building. The choice of location is certainly a very fortunate one, because as a sight in Berlin, it already exerts a certain attraction on the public. The rooms made available for the photography exhibition are on the first floor and are large enough to be able to arrange the numerous pictures etc. received in a clear order. Unfortunately, the lighting conditions are sometimes quite unfavorable, so that some beautiful pieces do not really come into their own. The exhibition itself is richly represented by all parts of the world, namely Austria, England, France and Belgium, which are countries that have participated heavily and are distinguished by their outstanding achievements, especially in artistic terms. (1.)

Left: The 1896 Official catalogue and guide of the International Exhibition for Amateur Photography Berlin, (Officieller Katalog und Führer der Internationalen Ausstellung für Amateur-Photographie Berlin 1896.) published by Rudolf Mosse, featured a cover drawing of a photographer and two farmworkers. The 112 pp. catalogue featured a frontispiece of the Reichstag, a listing of exhibits and 40 pages of advertising at the rear. Photo courtesy Antiquariat Geister, Berlin. Right: Printed in red letterpress are details that appeared opposite the title page to the portfolio “Nach der Natur” published in early 1897. Individual page: 48.5 x 35.2 cm. Translated, it reads: ALBUM ✻ OF THE INTERNATIONAL EXHIBITION FOR AMATEUR PHOTOGRAPHY BERLIN 1896 ✻ PUBLISHED ON BEHALF OF ✻ THE GERMAN SOCIETY OF FRIENDS OF PHOTOGRAPHY ✻ AND ✻ THE FREE PHOTOGRAPHIC ASSOCIATION ✻ BY ✻ FRANZ GOERKE ✻ ✻ ✻ ✻ ✻ ✻ ✻ ✻ ✻ ✻ ✻ ✻. From: PhotoSeed Archive
Wiener Photographische Blätter, Vienna: November, 1896: reviewer Ludwig David:
⎯ Respectfully withholding commentary for work shown at the exhibition by his own club: “the Vienna School has taken its place with honor”, David gives overall thoughts and then offers criticism for individual works at the exhibition from their respective countries, England, France, Belgium, etc: “The exhibition was divided into several sections in order to keep the representations of artistic photography and those serving scientific purposes separate. The fact that the exhibition was housed in the stately, wide rooms of the new Reichstag building ensured that it was well attended, as many people were enticed to get to know the interior design and the beauties of this new building. The large number of visitors, around 26,000 people, can also be attributed to the keen interest shown in the exhibition by Berlin’s upper class.
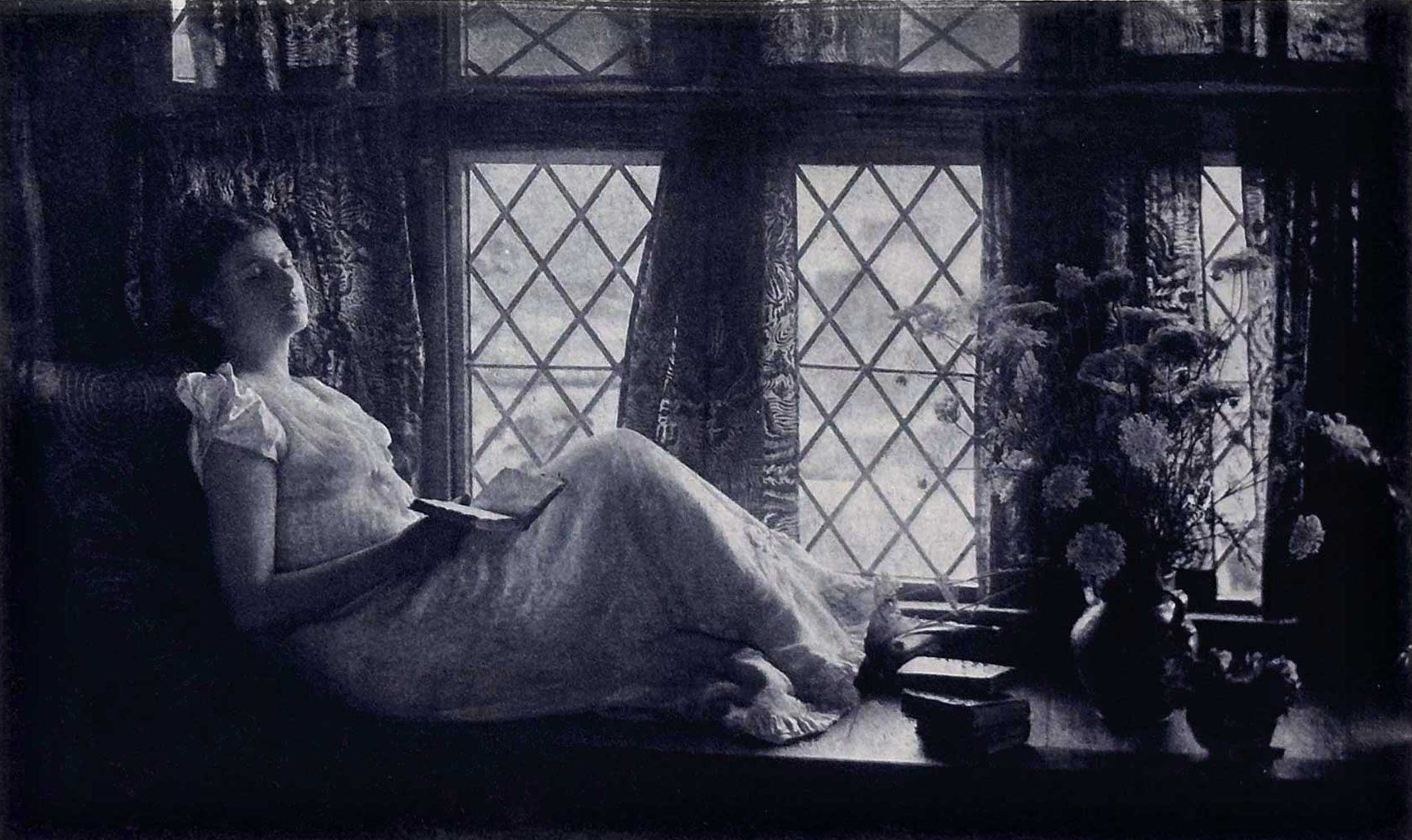

“ln der Dämmerung | At Dusk”: 1897” Emma Justine Farnsworth, 1860-1952: American: Hand-pulled photogravure, plate #3 included within letterpress for “Nach der Natur” portfolio: 8.4 x 14.0 cm on leaf 48.5 x 35.2 cm. This photo dates to 1893, and is a variant of a better known pose she copyrighted in 1894. (where subject is not sleeping) Vienna reviewer Ludwig David commented on Farnsworth work at the 1896 Berlin exhibition: “In Emma Justine Farnsworth (Albany) we meet an excellent artist whose figure studies are surrounded by a poetic magic. When one considers that the depiction of the figurative in the natural landscape is in itself a delicate task, one must doubly admire the lyricism associated with the pictures. The good pigment prints, produced in bright colors, also give the pictures a captivating charm. “At Dusk” is the title of one of the most beautiful Chiaroscuro pictures. A young lady is resting, stretched out on a bench, just below a window formed by bull’s-eye panes; the light floods in places.” Wiener Photographische Blätter, November, 1896 p. 214. From: PhotoSeed Archive
⎯ All of the pictures that were not for scientific purposes, there may have been several thousand of them, were housed partly in the corridors, which receive their scant light from the courtyards of the building, and partly in a large domed structure that connects these corridors and has a skylight. In these rooms there was room for all the pictures that are understood under the somewhat cumbersome and tasteless name of “amateur photographs.” There was no separation of the pictures of an artistic nature from the majority of pictures that do not claim this designation.”
⎯ From America, David singles out William Boyd Post, Clarence Moore, C.R. Pancoast, Charles I. Berg, Emma Justine Farnsworth, A. Eidenmüller (St. Paul) and Alfred Stieglitz: …“a well-known master whose fame was not first established at this exhibition. Most of his pictures are no longer new either. “A wet day, with its drastic rainy mood is outstanding; “Scurrying home“, two old Dutch women walking through the countryside, is picturesque, a splendid picture printed in sepia.
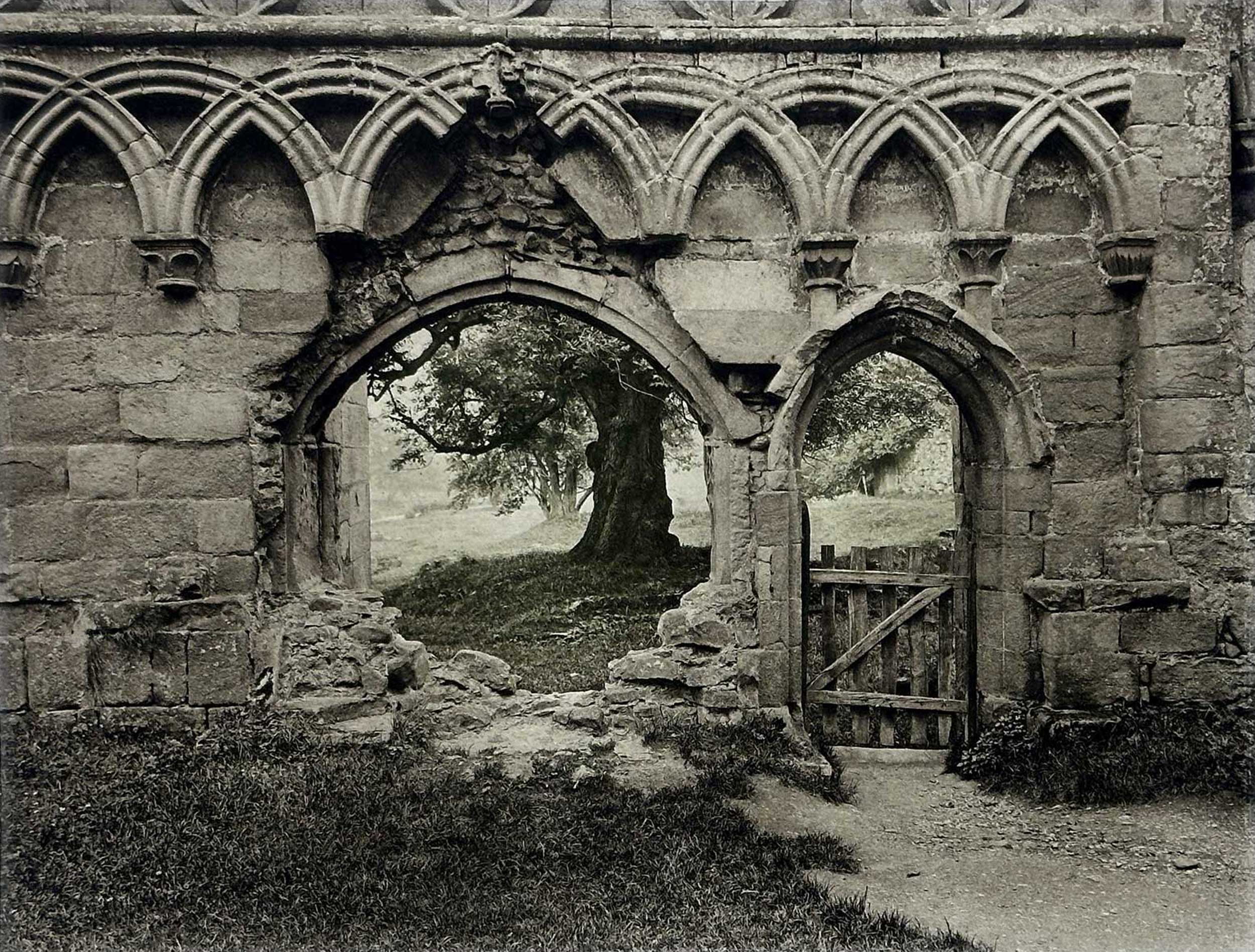

“Bolton Abbey”, Charles S. Baynton, 1866-1926: English: Hand-pulled photogravure, plate #10 included within “Nach der Natur” portfolio: 15.8 x 20.7 cm on leaf 35.2 x 48.5 cm. This stunning multiple-color photogravure is surely one of the highlights of the portfolio. C.S. Baynton was an accomplished amateur photographer who specialized in architectural work. He was a long-standing member of the Birmingham Photographic Society. Located in North Yorkshire, the historical remains of Bolton Abbey (monastery) date to the middle ages. From: PhotoSeed Archive
⎯ It must be said of the exhibition itself that it has fully fulfilled its task of giving a picture of the current state of photography. The arrangers, who had to deal with an enormous amount of material, deserve credit for having handled this task in a skilful manner: among others, Dr. Neuhauss has done particularly well for the scientific department of photography, and Mr. Franz Goerke for the artistic department. The light in the exhibition room was not sufficient in all places, the pictures were often too close together and hung much too high. It would also have been advisable to separate the pictures with a painterly effect from the works that were not of the same quality and to have the admission and award jury for this section comprise only recognized artists.” (2.)
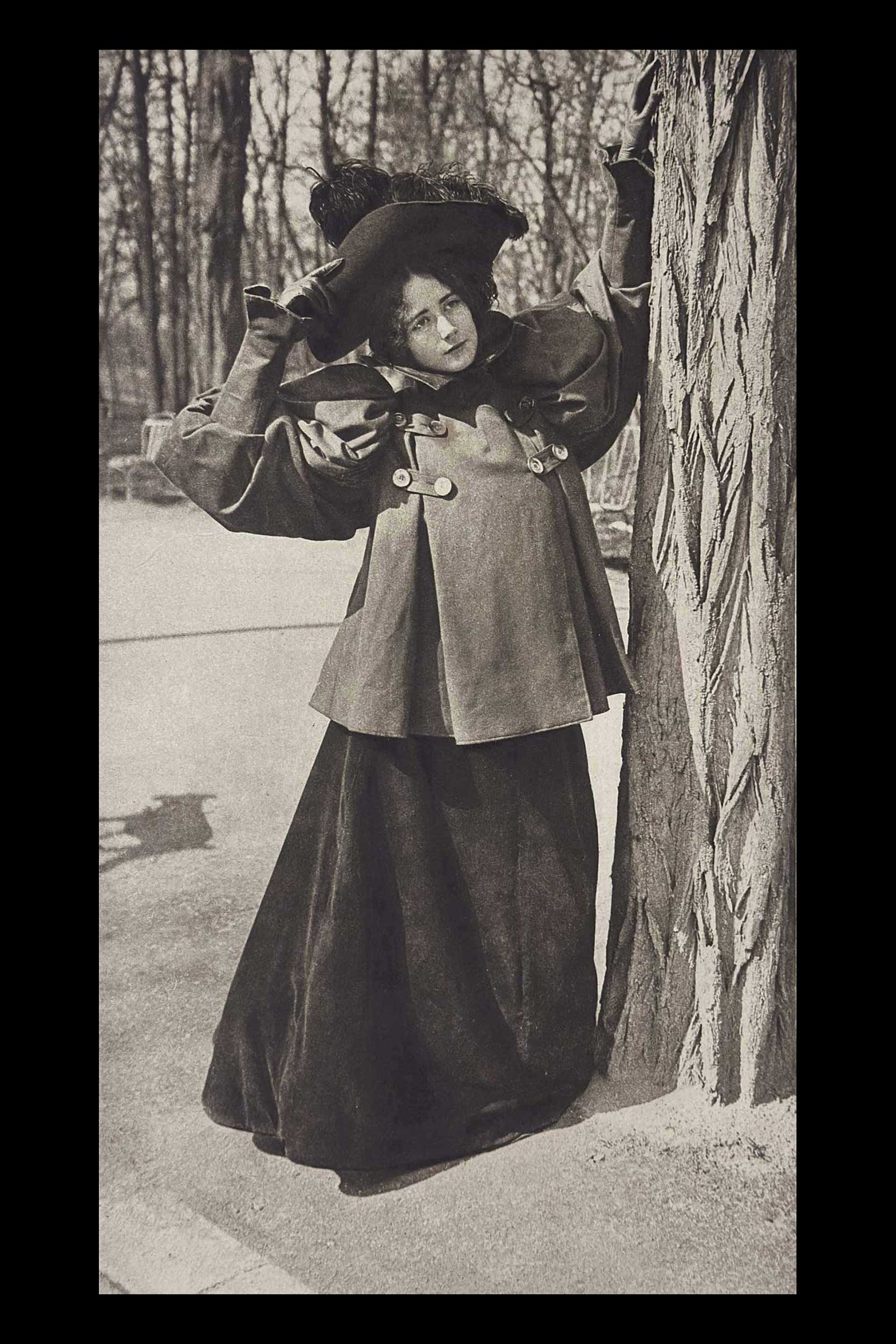

“Mlle. Cléo de Mérode”, Carle de Mazibourg, dates unknown: French: Hand-pulled photogravure, plate #8 included within “Nach der Natur” portfolio: 23.0 x 14.6 cm on leaf 48.5 x 35.2 cm. Amateur photographer Carle de Mazibourg is considered one of the very first street fashion photographers and since at least 1895 was a member of the professionally oriented Societé Française de Photographie Paris. His subject here-modeling in a Paris park, is French Belle Époque dancer Cléo de Merode. (1875-1966) Merode has been referred to as the “first real celebrity icon” and the “first modern celebrity”. She was also the first woman whose photographic image, due in particular to photographers Nadar and Léopold-Émile Reutlinger, was distributed worldwide. From: PhotoSeed Archive
Photographische Correspondenz, Vienna & Leipzig: October, 1896: Unknown reviewer(s):
⎯ Would you like a picture of the international exhibition for amateur photography in Berlin? If you call a horse a crocodile, you have used a nomenclature that is just as correct as calling this exhibition an amateur exhibition, assuming that you assume that the amateur does photography for pleasure.
It would actually be time to divide amateur photographers into two classes: amateurs who turn to the subject out of scientific interest and pursue serious studies for their own development, and dilettantes who only engage in photography per diletto, for pleasure and to pass the time. Even with this classification, the name of the exhibition would hardly be correct, because it contains universal material in which the specific arts and crafts play a large part; it shows the enormous expansion of photography in our time, of which portrait photography is only a very small individual case. Due to this versatility, one could say that the exhibition is filled with the work of professional photographers.
⎯ There is hardly an area of art and science that does not have a connection with photography. This explains the lively interest shown in this technique even in the highest circles, and which finds its most striking expression in the fact that Her Majesty the Empress Frederick has granted the exhibition her patronage.
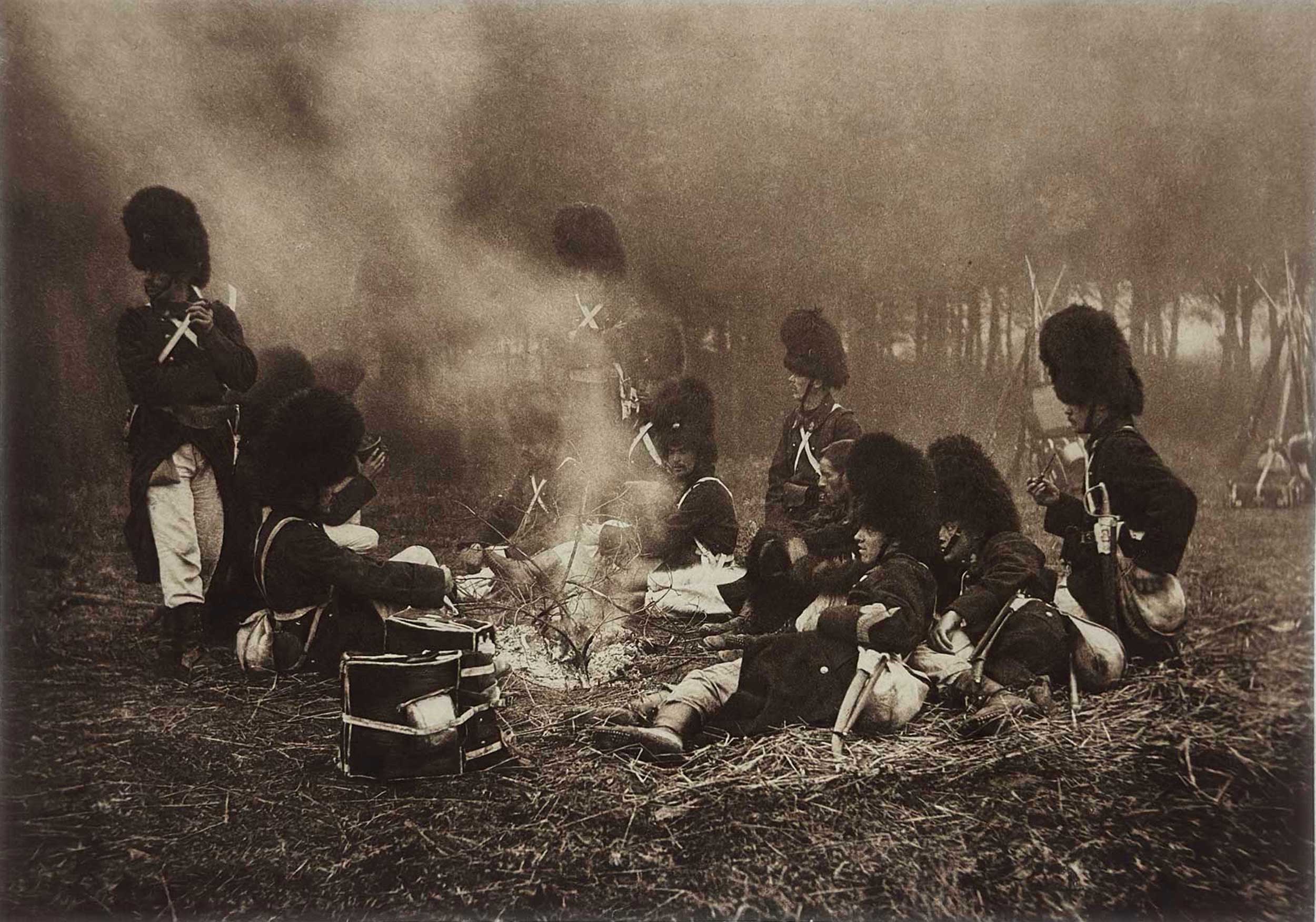

“Grenadiers at the Watchfire”: Albert-Edouard Drains, known professionally as Alexandre: 1855-1925: Belgian: Hand-pulled photogravure, plate #12 included within “Nach der Natur” portfolio: 20.2 x 28.6 cm on leaf 35.2 x 48.5 cm. Grenadier guard soldiers, (British? French?) their swords at their side, sit around a watchfire. In addition to being a renowned pictorialist: landscapes, seascapes, studies of military life, nudes, portraits of artists, etc., Alexandre was a Photograph dealer specializing in the collotype process of reproducing paintings in the Royal Museums of Belgium. From: PhotoSeed Archive
⎯ The exhibition not only gives a picture of art and science, no, it gives a description of the world in pictures, which ranges from the mists of emerging worlds to the tiniest creatures that treacherously gnaw at the health of our bodies; and those who are prevented by unfavorable circumstances from following their urge to travel far away will find satisfaction here, because Mother Earth is presented to them from the snow-covered peaks of the highest mountains to the deepest shafts of the burrowing miners, from the islands of the South Seas circling the globe to the west, to the magnificent landscapes of California.
⎯ On the whole, the practice of platinum and pigment processes predominate. Matte collodion paper is also often used, but cannot compete with the first-mentioned processes in terms of artistic impression, not least because of the bluish cold tone of the background, which is one of the disadvantages of stencil-based photography. Pictures with a glossy surface are only found in small numbers and least of all where the artistic effect of the picture is important.
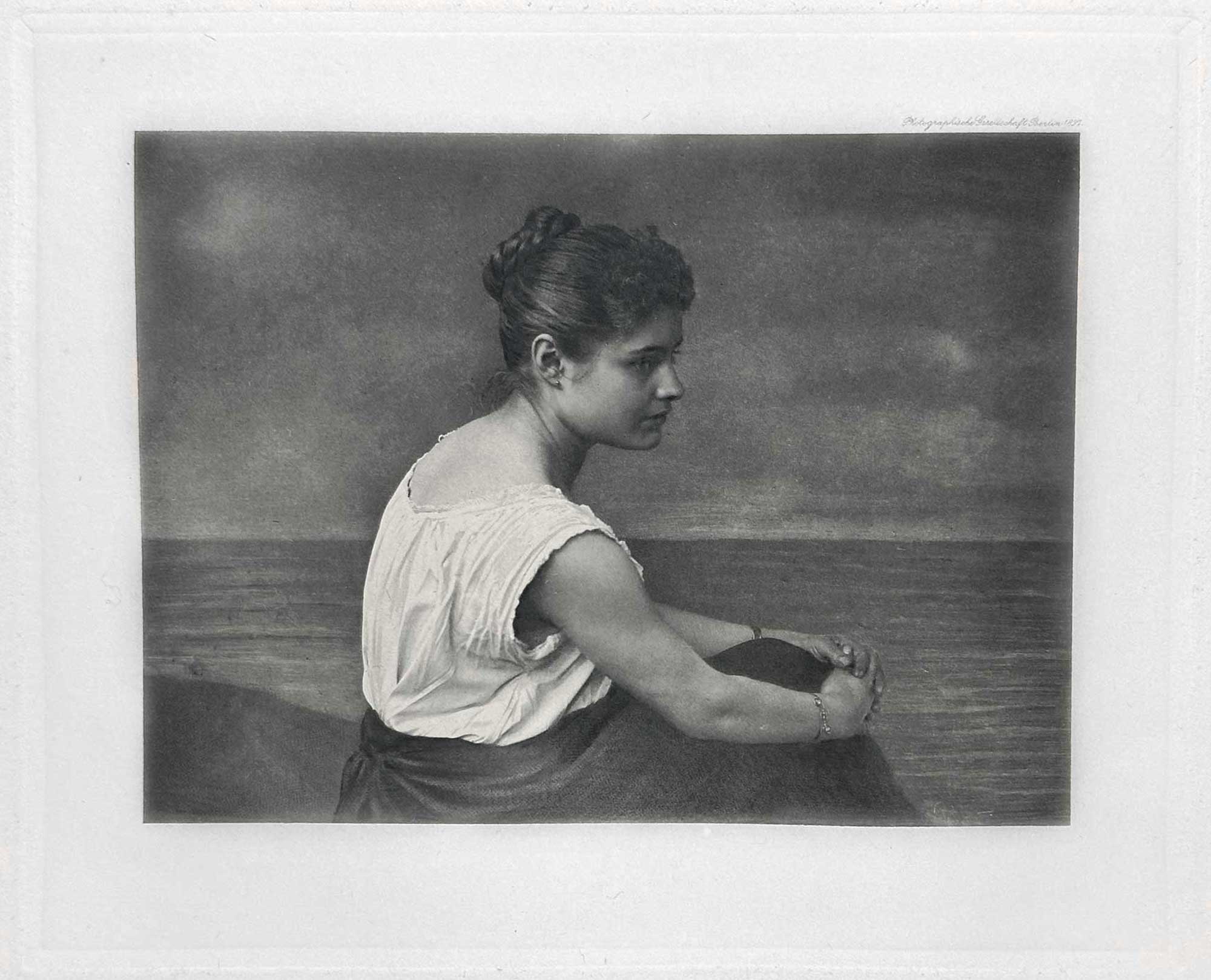

“Am Meere | By the Sea”: Rudolf Crell: 1833-1904: German: Hand-pulled photogravure, plate #12 included within “Nach der Natur” portfolio: 11.9 x 16.0 cm on leaf 35.2 x 48.5 cm. A painted seashore behind her, a woman poses for a portrait inside a studio. Rudolf Crell was known to also be a painter, so the backdrop may be by his hand. A senior teacher ,Crell lived in Altona from 1875. He was a full member of the Society for the Promotion of Amateur Photography in Hamburg from 1895 until he moved to Desau in 1898. From: PhotoSeed Archive
⎯ We now enter the round domed hall, which has an international character. We would like to call it the fermentation vat of the exhibition, because here it ripples and foams and struggles for new means of expression and creates bubbles, some of which disintegrate, while others condense into core points around which new structures arrange themselves. Here you can hear the professional photographers cry out in horror, and yet they should be able to explain why a considerable number of visitors describe these works in particular as painterly and virtuosic. Does the secessionist idea have any justification alongside the traditional art forms? It undoubtedly deserves to be examined for its causes, its nature and its relationship to the traditional. It is the absolutely unfamiliarity that has a repulsive effect on the professional photographers here. They are used to looking at the world through photographic glasses and do not believe that it looks completely different in reality. But photography is old enough that these glasses will need new lenses that are a bit sharper. A picture that is hung on the wall must not be too small and must have a different, less decorative character than a picture that is kept in an album for intimate viewing. For this reason, the large pictures at the exhibition are so much more effective than the small pictures that one has to look at with a trained eye. (3.)
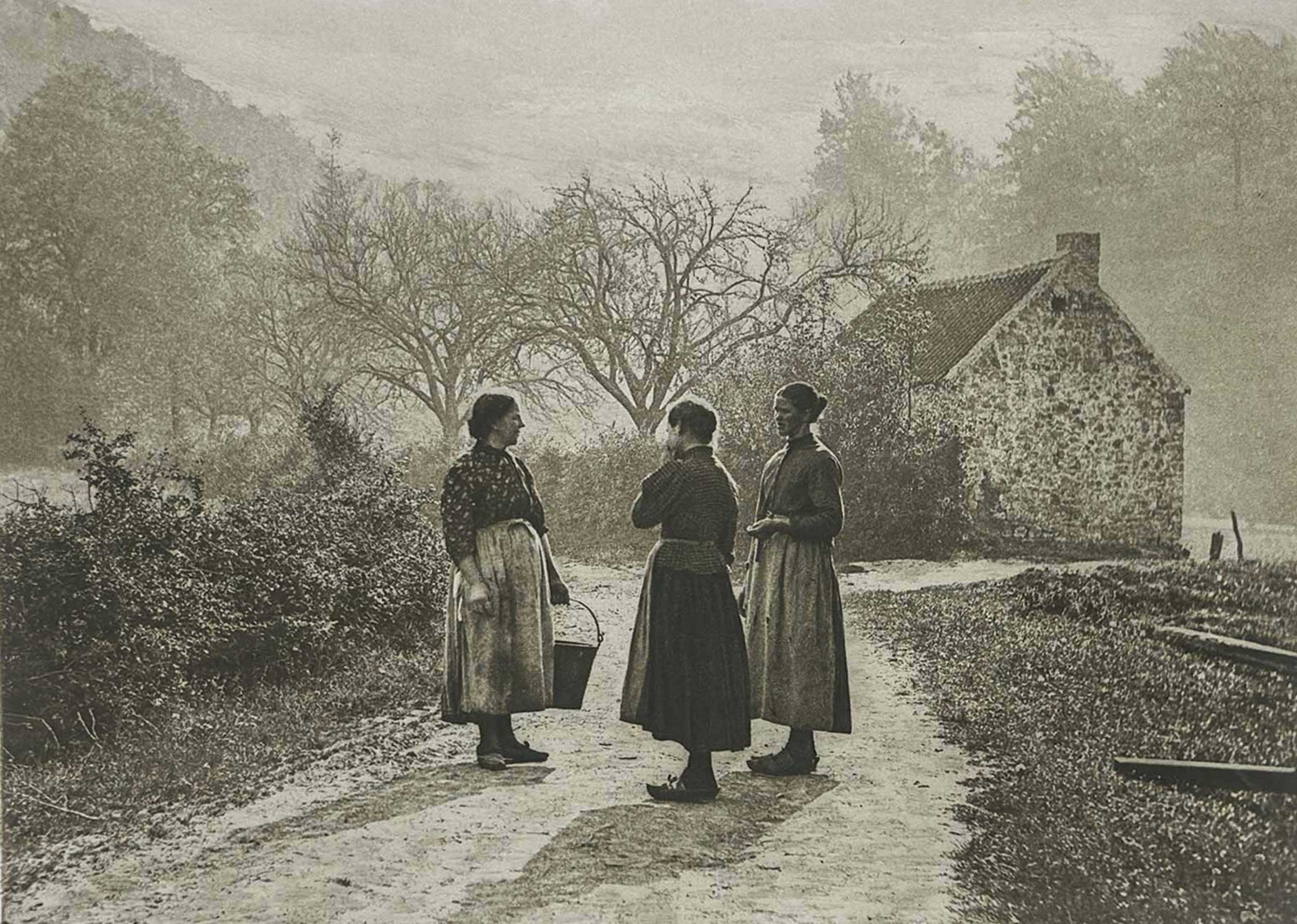

“Auf der Landstrasse | On the Country Road”: Léonard Misonne: 1870-1943, Belgian: Hand-pulled photogravure, plate #22 included within “Nach der Natur” portfolio: 15.4 x 21.1 cm on leaf 35.2 x 48.5 cm. Three women gather to chat on a country road outside their village- a welcome interlude perhaps for chores begun. According to the Directory of Belgian Photographers, “Misonne’s work is characterised by a masterly treatment of light and atmospheric conditions. His images express poetic qualities, but sometimes slip into an anecdotal sentimentality.” He was nicknamed “the Corot of photography”. From: PhotoSeed Archive
Compatriots in Photogravure: Franz Goerke & Alfred Stieglitz
And who was responsible for these “sumptuous hand-pulled photogravure plates” contained in Nach der Natur? The Photographische Gesellschaft in Berlin. As I’ve noted elsewhere on this site, the proper name of this atelier is The Berlin Photographic Company. Established in 1862 in Berlin, Germany with retail and distribution branch offices located in New York, London and Paris, this large art publishing house was founded by the brothers Christian “Albert” Eduard Werckmeister, (1827-1873) an engineer and chemist, and “Friedrich” Gustav Werckmeister, (1839-1894) a painter and etcher. The concern was collectively owned and run by their younger brother Emil Werckmeister. (1844-1923) The majority of their efforts concerned the reproduction and sale of engravings and notable oil paintings by master artists in the collections of major museums and collections throughout Europe, with the permanent process of photogravure a specialty of the house.
The establishment of fine photogravure production in Europe, including the earlier noteworthy efforts of Walter L. Colls in London for his Linked Ring Salon folios and Photo Club de Paris folios by Charles Wittmann in Paris set a very high bar for the future published efforts of Franz Goerke in Berlin and Alfred Stieglitz in New York.
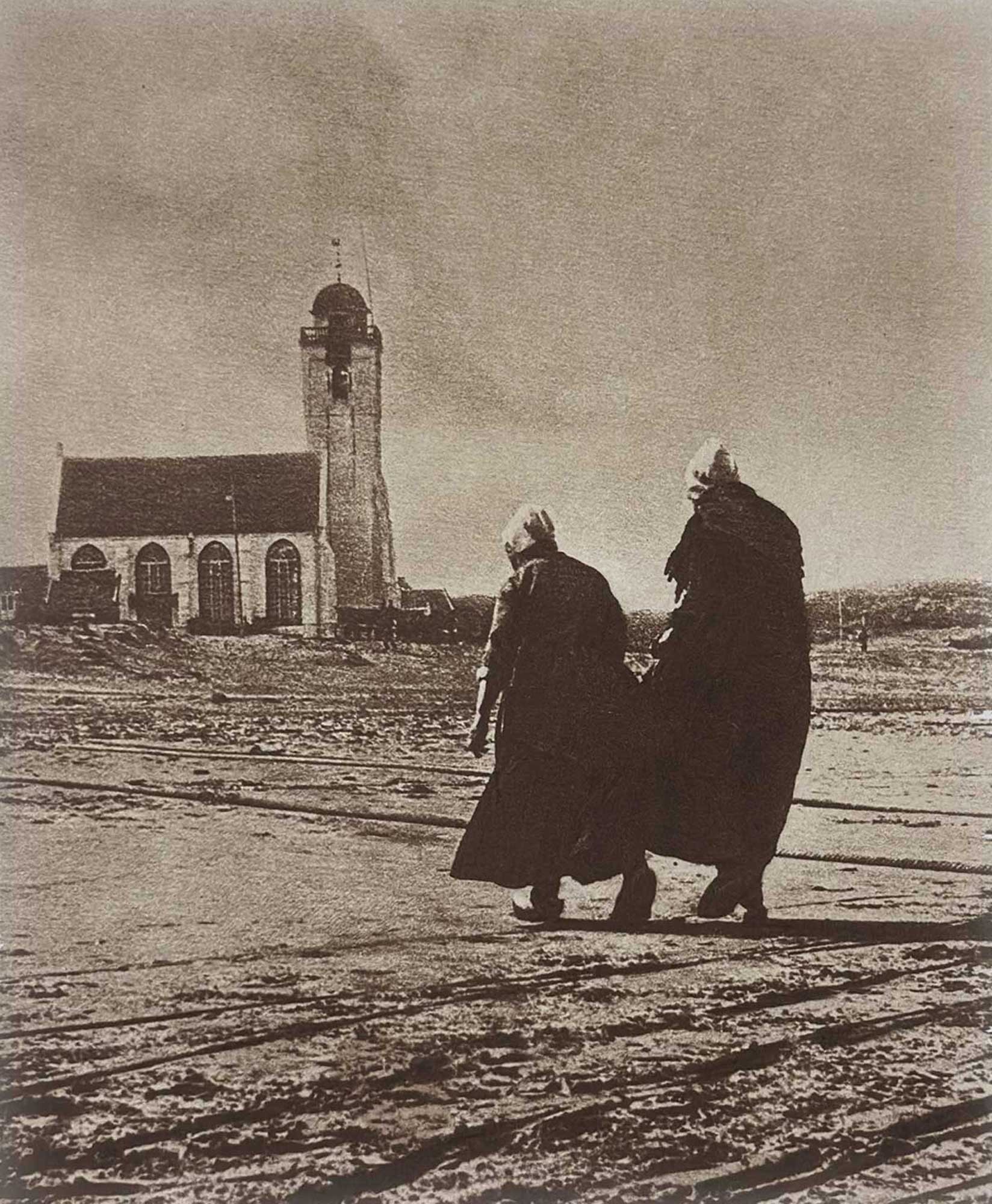

“Nach Hause | Home”: Alfred Stieglitz: 1864-1946, American: Hand-pulled photogravure, plate #30 included within “Nach der Natur” portfolio: 18.9 x 15.6 cm on leaf 48.5 x 35.2 cm. Dutch fishwives head for home on the beach at Katwyk, in South Holland. Best known with the title Scurrying Home, its alternate title is Hour of Prayer, the implication being they were heading to their daily ritual of the sanctuary of the church-seen in the background of the photograph. From: PhotoSeed Archive
After his publication of Nach der Natur, Goerke, (1856-1931) an important exponent of German art photography, took on the project of being editor and publisher for Die Kunst in der Photographie, (The Art of Photography) published in Berlin from from 1897-1908. Many of the hundreds of fine photogravure plates making up the run of DKIDP beginning with 1897 can be found in this archive. A founder along with others in 1889 of the Free Photographic Association in Berlin, Franz Goerke’s promotion of photography as art is summed up as part of his Preface to Nach der Natur:
“The seed has been sown by this exhibition. May it bear rich fruit. Above all, it should convince those who still see artistic photography as a useless and pointless game that there is a deep and serious desire in amateur circles to raise photography to the status of art and to place it alongside other arts.”
An amateur photographer himself, Goerke’s passion as publisher and editor certainly piqued the interest of Alfred Stieglitz (1864-1946) in New York, a self-taught amateur photographer whose formal education included mechanical engineering, beginning in October, 1882, when he enrolled in the all male Technical University of Berlin (Technische Hochschule) and later photochemistry at the same institution- taught by Hermann Wilhelm Vogel. (1834-1898) An authority on orthochromatic photography, Vogel became a mentor to the young Stieglitz, and he later founded the Deutsche Gesellschaft von Freunden der Photographie (German Society of the Friends of Photography) in 1887.
At the conclusion of his university studies and Continental wanderings, Stieglitz returned to the US in September, 1890 at the passing of his sister Flora. At the urging of his father Edward, he soon became involved with the business venture of photoengraving: first at the struggling Heliochrome Company in lower Manhattan, which he eventually restructured. Taking on his two former Berlin roommates Louis Schubart and Joseph Obermeyer as partners, this concern was rechristened the Photochrome Engraving Company. Photogravure was a specialty, but Stieglitz soon became involved in other ventures-first co-editing the American Amateur Photographer in 1893, ultimately rising to sole editor in January, 1895, the increased workload among his other interests giving him “the opportunity to disentangle himself from the Photochrome Engraving Company”. (4.) Even without having a direct hand in his own atelier, by the time he received his copy of the Nach der Natur portfolio in late 1897, his obvious delight and respect for the photogravure plates executed within by the Photographische Gesellschaft in Berlin under Goerke’s mindful watch gave him obvious delight. This in turn gave him reason to author a review of the portfolio in the pages of the new publication Camera Notes, the journal of the New York Camera Club. Paraphrasing, his reaction to the quality of these plates proclaimed photogravure: “the most perfect of all photographic reproduction processes.” (5.)

“Photographische Gesellschaft Berlin”: gold emblem, (5.0 x 3.9 cm) stamped on verso of cloth-covered boards for Nach der Natur portfolio. (49.8 x 37.0 x 2.2 cm) Known as the Berlin Photographic Company, this atelier, a large art publishing house, was established in 1862 in Berlin, Germany with retail and distribution branch offices located in New York, London and Paris. The permanent process of photogravure was a specialty of the house, and it was chiefly concerned with the reproduction and sale of engravings and notable oil paintings by master artists in the collections of major museums and collections throughout Europe. From: PhotoSeed Archive
The review in its entirety: “Nach der Natur” is without doubt the most elaborate and beautiful publication which has yet appeared in photographic literature.
The series of photogravures which form the bulk of the book, include pictures by the chief medallists of the Exhibition. Among the familiar names we find: Henneberg, Alexandre, Hannon, Farnsworth, Stieglitz, Le Beque, Bremard, Baynton, Esler, David, Boehmer, etc. The text, which serves as an introduction to the pictures, is an essay, which tries to prove that pictorial photography may be an art. Even if all the pictures selected may not prove the case most of them are perfect gems. The photogravures, as such, are beautiful specimens of the most perfect of all photographic reproduction processes.
The library of every photographic club should include this important work, as those interested in pictorial photography will find every phase of it well represented. A copy has been procured for the Camera Club Library. A.S. (6.)
Stieglitz would go on to publish his own portfolio of fine photogravures: Picturesque Bits of New York and Other Studies in 1897, (N.Y.: R.H. Russell) the same year Nach der Natur appeared. On the other side of the Atlantic, Goerke’s own Die Kunst in der Photographie, which should be considered the most important European publication directly inspiring the fine photogravures that soon appeared under the editorship of Stieglitz’s Camera Notes, would in turn lead him elevating the process to its apogee in the US: his groundbreaking and seminal venture Camera Work, published between 1903-17.
⎯ David Spencer October, 2024
1. Excerpt: Paul Hanneke: Internationale Ausstellung für Amateur – Photographie zu Berlin , Photographische Mitteilungen, Berlin: October, 1896: pp. 205-209/ continues: pp. 219-224; 235-37.
2. Excerpt: Ludwig David: “Die künstlerische Richtung auf der internationalen Ausstellung für Amateur-Photographie in Berlin,” Wiener Photographische Blätter, Wien: 3:11 (November 1896), pp. 201–215
3.Excerpt: “Berliner Nachrichten. September 1896.”, Photographische Correspondenz, Vienna & Leipzig: October, 1896: from unknown reviewer(s): (article signed: “Von der Hasenhaide”) pp. 471-477
4. Julia Thompson: Stieglitz’s Portfolios and Other Published Photographs: Alfred Stieglitz Key Set, NGA Online Editions, accessed September, 2024
5. Camera Notes, New York: Vol. 1, issue III: January, 1898
6. Ibid, p. 85



