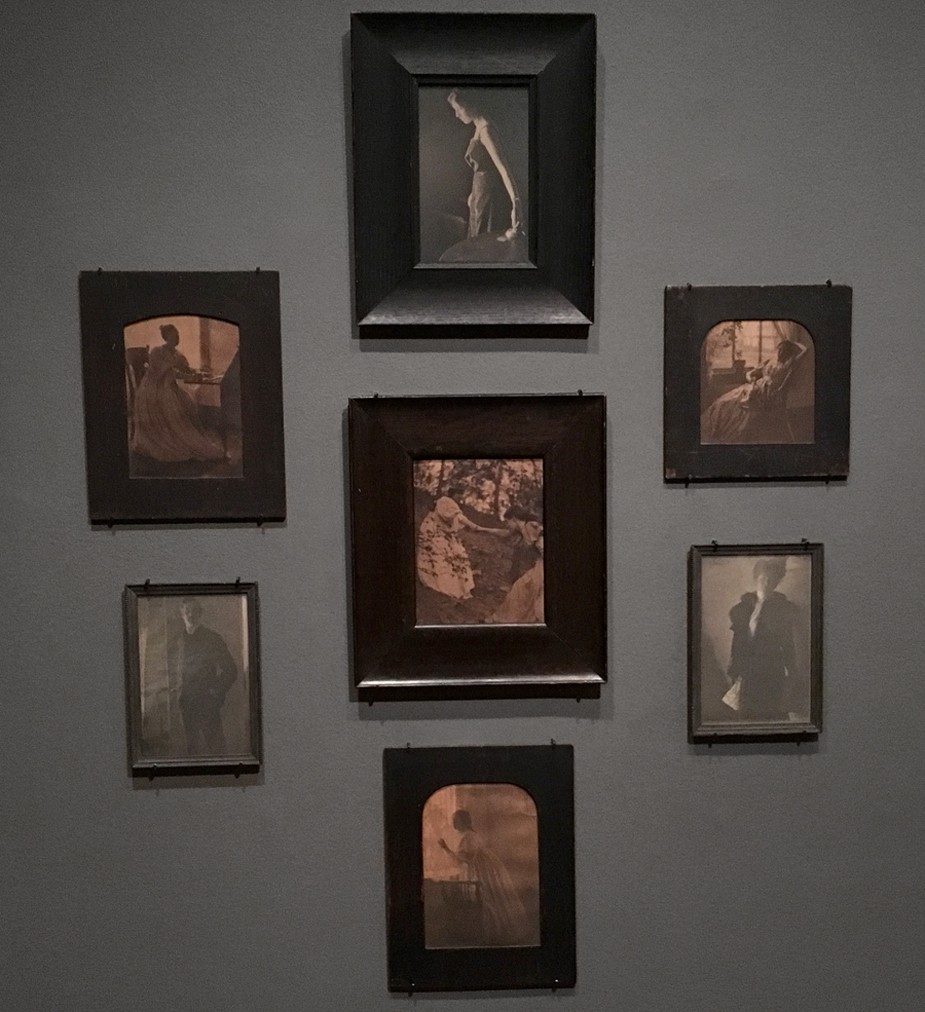
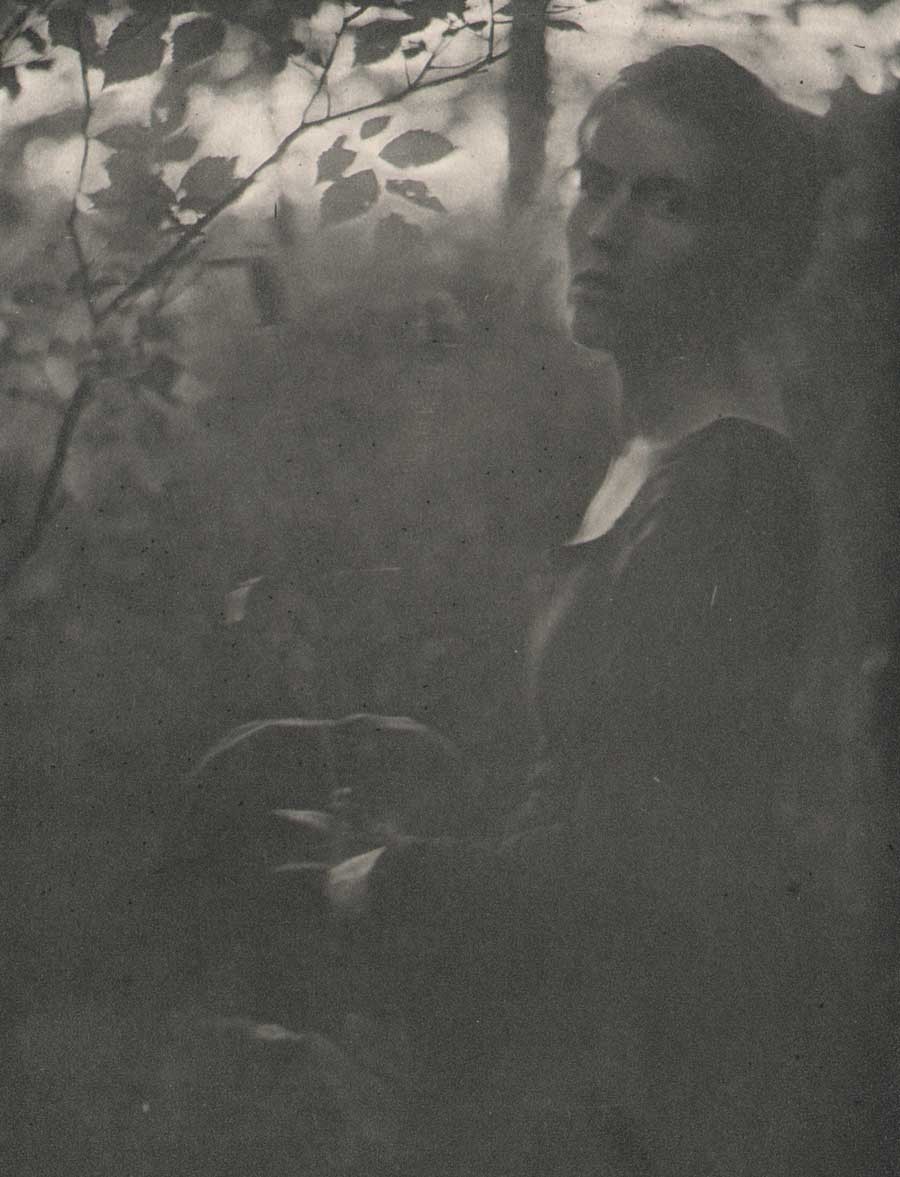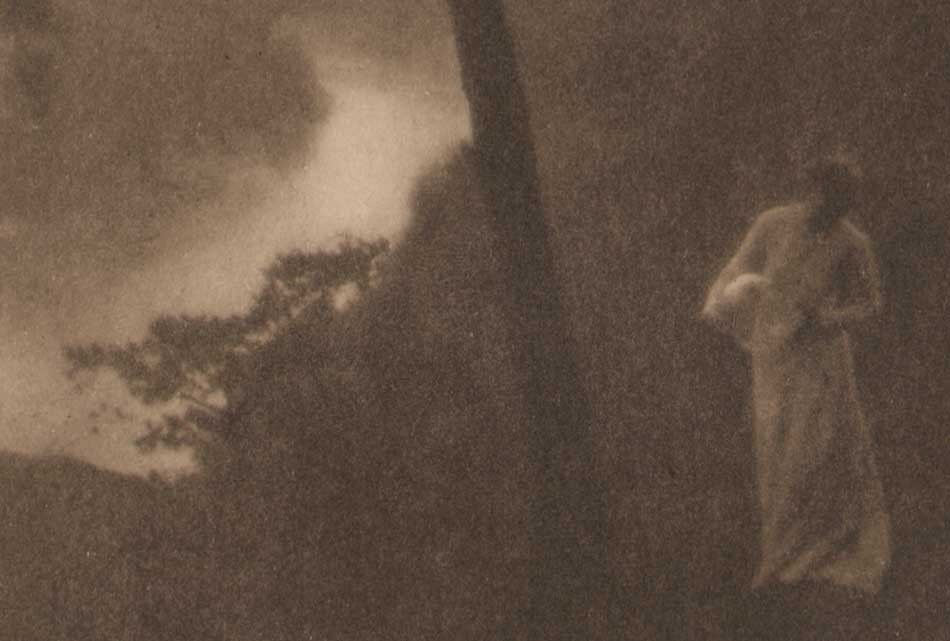Like the mythological bird the Phoenix, the groundbreaking photography and art journal Camera Work edited and published by Alfred Stieglitz of New York from 1903-17 is now available for purchase as a full run after long being out of print.

Rare Camera Work Ephemera: Left: This blank Camera Work subscription form for the year 1905 was mailed by publisher Alfred Stieglitz to photographer C.M. Shipman in Brooklyn, New York. (145 Milton St.) recto: 15.9 x 9.9 cm | opened: 9.9 x 19.8 cm | printed on Japan paper. Upper Right: The original mailing envelope (8.7 x 10.8 cm) addressed to Shipman in Stieglitz’s hand is stamped with a New York postmark of December 22, 1904. Lower Right: Another similar envelope addressed to photographer Adolph Petzold in Philadelphia and postmarked New York, September, 1904 is engraved on the verso: Alfred Stieglitz- 1111 Madison Avenue – New York. From: PhotoSeed Archive
Remarkably and metaphorically, this bird, capably guided by St. Louis resident Pierre Vreyen, has risen again even though its first creator, while acknowledging the passion it took to create it was a most admirable thing, nonetheless went on to dispose of at least one known full run of Camera Work by setting it alight in 1929 at his Lake George estate. In 1933, writing in a two-page letter on July 10 from there to writer and critic Lewis Mumford, Stieglitz outlines the emotional capital he expended on his involvement with and creation of Camera Work:
“Four years ago the complete set of Camera Work I had had up here for years I offered to the Evening Star. It was a wonderful sight to watch the volumes burn. As you know books burn slowly…What a continuous heartache Camera Work represented & what blood was spilled over each issue fighting printers & fighting engravers—fighting paper dealers & paper manufacturers—fighting ink manufacturers & binders—fighting those who did the packing—fighting the post office—every step I controlled personally—as I sat there & realized what passion it all represented—I had to smile at myself.—Ye gods what won’t passion do.” (1.)
Originally from Liege, Belgium and trained as an electrician and draftsman but more recently plying his trade as a commercial photographer, Pierre explained to me his inspiration for bringing Camera Work back to life, so to speak:
“It all started when Mark (Katzman) said he would love to have a digital copy of Camera Work so he could open it anytime without the fear of over-manipulating his set of originals. I told him I would give him a hand doing it and it took 2 years to make.”
With the establishment of his website cameraworkmagazine.com, which includes short videos of him leafing through each newly published issue of Camera Work, one can order the full run of the journal in facsimile: the most complete and faithful copy of the original ever published. The cost is $1200, which includes a separate index issue, plus shipping.

“Earliest known Camera Work Sales Catalogue” ( post publication): ca. 1924, uncoated paper: 13.8 x 10.1 cm (Cover). New York: E. Weyhe Gallery. This small pamphlet shows a facsimile of the CW cover at left while opened to the first gatefold at right. The prospectus by the E. Weyhe Gallery, located at 794 Lexington Avenue in New York City, reprinted press notices for CW along with a synopsis of available issues and prices, including the final Paul Strand double issue 49-50 from 1917 for $17.50: An excerpt: “We Have recently obtained from the publisher a large stock of Camera Work, the remainder of this unique chance to obtain copies, both singly and in sets. Many of these numbers had already become scarce, and there never will be an opportunity to obtain so large a selection again.” From: PhotoSeed Archive

“Synopsis of Numbers: 1-22”: “Earliest known Camera Work Sales Catalogue” ( post publication): ca. 1924, uncoated paper: 13.8 x 20.1 cm (this gatefold). New York: E. Weyhe Gallery. The prospectus by the E. Weyhe Gallery, located at 794 Lexington Avenue in New York City, reprinted press notices for CW along with a synopsis of available issues and prices, including the final Paul Strand double issue 49-50 from 1917 for $17.50: An excerpt: “We Have recently obtained from the publisher a large stock of Camera Work, the remainder of this unique chance to obtain copies, both singly and in sets. Many of these numbers had already become scarce, and there never will be an opportunity to obtain so large a selection again.” From: PhotoSeed Archive

“Synopsis of Numbers: 23-48; 49-50; 2 special issues and special large plate gravure of The Steerage”: “Earliest known Camera Work Sales Catalogue” ( post publication): ca. 1924, uncoated paper: 13.8 x 20.1 cm (gatefold at left and back cover at right: 13.8 x 10.1 cm ). New York: E. Weyhe Gallery. The prospectus by the E. Weyhe Gallery, located at 794 Lexington Avenue in New York City, reprinted press notices for CW along with a synopsis of available issues and prices, including the final Paul Strand double issue 49-50 from 1917 for $17.50: An excerpt: “We Have recently obtained from the publisher a large stock of Camera Work, the remainder of this unique chance to obtain copies, both singly and in sets. Many of these numbers had already become scarce, and there never will be an opportunity to obtain so large a selection again.” From: PhotoSeed Archive
Pierre says: “The aim of this project is to put (Camera Work) in the hands of schools, teachers, students, museums, libraries, collectors, appraisers, auction houses, individuals, etc… a high quality reproduction of the originals at a reasonable price.”
Intrigued, I asked him what some of the challenges were for pulling the project off, and I couldn’t help but think of parallels Stieglitz himself surely encountered, yet updated for the digital age:
“There were many challenges. At first was where to start? From what? Luckily I found the Modernist Journal Project online which has a digital copy of Camera Work. It is incomplete but we contacted them and they were kind enough to supply us with their raw files. I used their files for the text pages but not for the plates.
The text pages needed a lot of work in Photoshop to clean, resize, straighten, etc… and then we had to photograph many of the plate pages Mark (Katzman) had no high res files in his archive. I also had to align the often found ghost image present on the facing page of the plates. Look at the video clips I have on the website and you’ll see what I mean. Especially visible in number 49-50.”
Continuing, and with the knowledge he has put up a significant amount of his own money to complete 25 full sets of Camera Work, Pierre spoke of finding someone to print the issues, something that happens less and less in this digital age:
…“I had to find a printer. I first looked online but the choices are limited and it ends up getting expensive really quick when you want to use a print on demand service like blurb.com. So I looked locally.
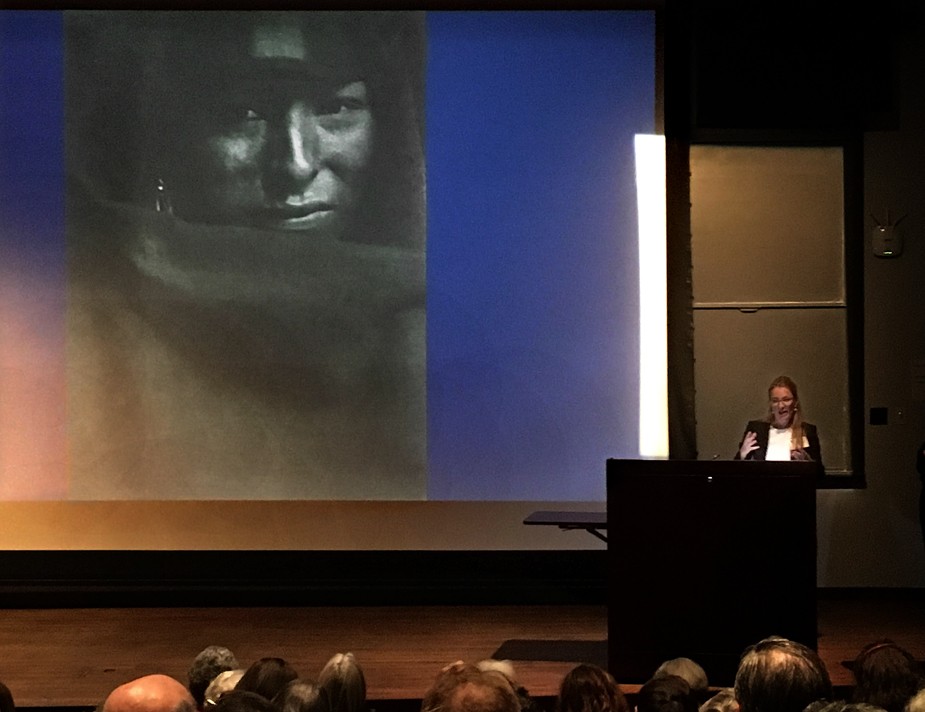

International Camera Work Scholarship: With “The Red Man”, a head study reproduced as a photogravure plate in Camera Work I by Gertrude Käsebier from 1903 projected on the screen at left, Professor Dr. Bettina Gockel, principal investigator for the project Camera Work: Inside/Out at the University of Zurich from 2015-18 delivers her paper: “More Than Genius: The Invention of Photographic Genius and the Importance of the Journal Camera Work” during the symposium Rethinking “Pictorialism”: American Art and Photography, 1895 to 1925 at Princeton University in October, 2017. Photo by David Spencer for PhotoSeed Archive
I found a printer that was in St. Louis but after many, many weeks of proofs and tries, it did not work out. Back to square 1, I found another printer about 80 miles from St. Louis and this is the one I ended up using. All in all, it took me 6 months dealing with different printers to finally get what you saw in Rochester, the final product.”
As an added bonus, Pierre will also sell you a piece of history from the pages of Camera Work: approximately 180 individual advertising pages from the journal are listed on his site and can be ordered as 16 x 20″ framable art prints for the bargain of $30 each.
Would the master Approve?
Not that my opinion matters, but here goes. It’s hard to guess if Alfred Stieglitz would have embraced the concept of digitization. My hunch says no, because I want to believe one of the most important legacies he left the world, Camera Work magazine, was something he would have been insistent be appreciated in its’ original form.
All well and good if you can get ahold of vintage copies, or have the tenacity and financial resources to acquire a full run of the 50 issues and supplements. But to those of us in the 21st century, the importance of the groundbreaking nature of the journal as well as the superb photogravure plates contained within give many of us ample reason to collect at least a few of the plates.

Published Literature: Camera Work: A chronological timeline of significant works are seen left to right: 1973: “Camera Work: A Critical Anthology” by Jonathan Green. This was the first significant evaluation of Camera Work, with an emphasis on the articles and text rather than the reproductions; 1973: “Camera Work: A Photographic Quarterly Edited and Published by Alfred Stieglitz, New York”. Published by the Minneapolis Institute of Arts, this volume accompanied the exhibition, “I Am an American,” that traveled to more than a dozen towns in Minnesota on the Minneapolis Institute of Arts’ Artmobile; 1978: “Camera Work: A Pictorial Guide” by Marianne Fulton Margolis was the first instance all 559 plates from Camera Work were published in a single-volume reference; 1997: “Camera Work- The Complete Illustrations 1903-1917”. Published by Benedikt Taschen with an essay by Pam Roberts additionally translated into German and French, it featured all plates taken from a complete set of the journal owned by the Royal Photographic Society, Bath; 2003: “Camera Work: A Centennial Celebration”: In celebration of the 100th anniversary of the publication of Camera Work, a traveling exhibition was organized by Stephen Perloff, editor of The Photo Review and The Photograph Collector. From: PhotoSeed Archive
Speaking personally, a delicate japan tissue gravure of a collaborative effort by Stieglitz and Clarence White from Camera Work was one of my very first photographic purchases as a collector. I convinced myself I would frame that photograph and hang it on the wall, but it slowly drifted to the bottom of an acid-free case as I rapidly descended into the madness of collecting vintage photographs, never to look back.
For the sake of historical context, a timeline of the most notable publishing efforts promoting Camera Work scholarship, although certainly not exhaustive given the hundreds, perhaps thousands of citations for the journal not listed here, are necessary for the record, and reveal ample support and evidence for Pierre Vreyen’s efforts at getting it back in print. I’ve also included a few links at the end of this post for some exciting recent scholarship and digitization efforts.
Camera Work: Key Dates & published Literature
1903-1917:
Issued quarterly in New York by Alfred Stieglitz, (1864-1946) the journal featured a cover design by a young Edward Steichen who created the Craftsman inspired typeface logo anchored by an outlined box: “A Photographic Quarterly* Edited And Published By * Alfred Stieglitz New York“. Steichen’s efforts included the overall design aesthetic for the interior pages, which even extended to the advertising pages published in the back of each issue. Through primary sources, Camera Work is known to have had a larger subscriber base when it was first introduced in the first decade of the 20th Century but waned considerably with the outset of World War I in Europe. In a three page letter written by Stieglitz to the writer and critic Lewis Mumford dated October 15, 1935, he states the size of the edition for individual issues while giving other valuable information on the albatross Camera Work had become to him, along with the solution:
“Camera Work has gone off to you in 4 packages by parcel post…As for the missing Plates they were not torn out of the books but were never put into those copies. You see many of the gravures were tipped in my hand (by me) after the numbers had been printed & bound. And I only completed the number of copies as were subscribed for. The edition was always 1000 copies except 49–50—that was 350. When I destroyed about 10000 copies of Camera Work—they were smothering me—I destroyed virtually all the Plates that had not been used. That’s why I can’t complete your incomplete copies.” (2.)

Vintage or Modern? Bottom Left: This mounted photogravure plate in Camera Work I from 1903 titled “A Study in Natural History” is by the American photographer A. Radclyffe Dugmore. This vintage example is opened to show it in relation to the opposing text page in an incomplete copy owned by the PhotoSeed Archive. Upper Right: The same page spread featuring the Dugmore plate in a new issue of Camera Work published as part of a set in May, 2018 and sold by Pierre Vreyen. Keen observers will notice the plates are flipped: this is because Alfred Stieglitz personally hand-tipped the gravure plates into each unique issue of Camera Work with the results sometimes being different in relation to placement on the plate pages. From: PhotoSeed Archive
1924: (ca.) After 1917, the first known marketing efforts for the journal appear by the E. Weyhe Gallery of New York City. They publish a small prospectus which served as a sales catalogue after buying up remaining copies from Alfred Stieglitz. Scans of an original prospectus owned by PhotoSeed can be seen above. In 2012, one was also included with the sale of a full leather-bound run of the journal by Sotheby’s. The auction house provided the following background on the Weyhe firm as part of the listing:
“New York art dealer and publisher Erhard Weyhe (1882-1972), whose gallery and bookshop on Lexington Avenue promoted not only prints and art books, but also photography. Weyhe and Stieglitz were friends who frequented each other’s gallery and worked with some of the same artists. Laid in the present set’s first volume is a prospectus issued by the Weyhe firm, announcing that ‘we have recently obtained from the publisher a large stock of Camera Work, the remainder of this unique publication, and we are now offering the public a chance to obtain copies, both singly and in sets.” (3.)
1969: The first attempt at a true duplication for the journal was undertaken by Kraus Reprint, (Nendeln/Liechtenstein) and is outlined by scholar Meredith A. Friedman for her 2009 master of arts thesis “Camera Work And The Alfred Stieglitz Collection At The Metropolitan Museum Of Art“:
“Camera Work was published in fifty volumes from 1903 to 1917. In 1969 Kraus Reprint reproduced all fifty issues of Camera Work in a six-volume set. The reprint is not a facsimile, but rather a duplication of the content (text and illustrations) of Camera Work page-by-page. The page size of the reprint editions is slightly smaller than the original issues. In an introductory note, the publishers explain that the reproduction was printed “as a service to scholars. It records the entire content of the original number, but does not attempt to reproduce its visual quality, nor the calibre of its plates.” (32) The Kraus Reprint edition of Camera Work seems to be the first time anyone acknowledged the value of Camera Work from a scholarly perspective.” (Editors note: Hathi Trust Digital Library currently has around 40 of the Kraus issues which can be accessed here.)
(32.) Alfred Stieglitz, Camera Work (Nendeln, Liechtenstein: Kraus Reprint, 1969), edition notice.
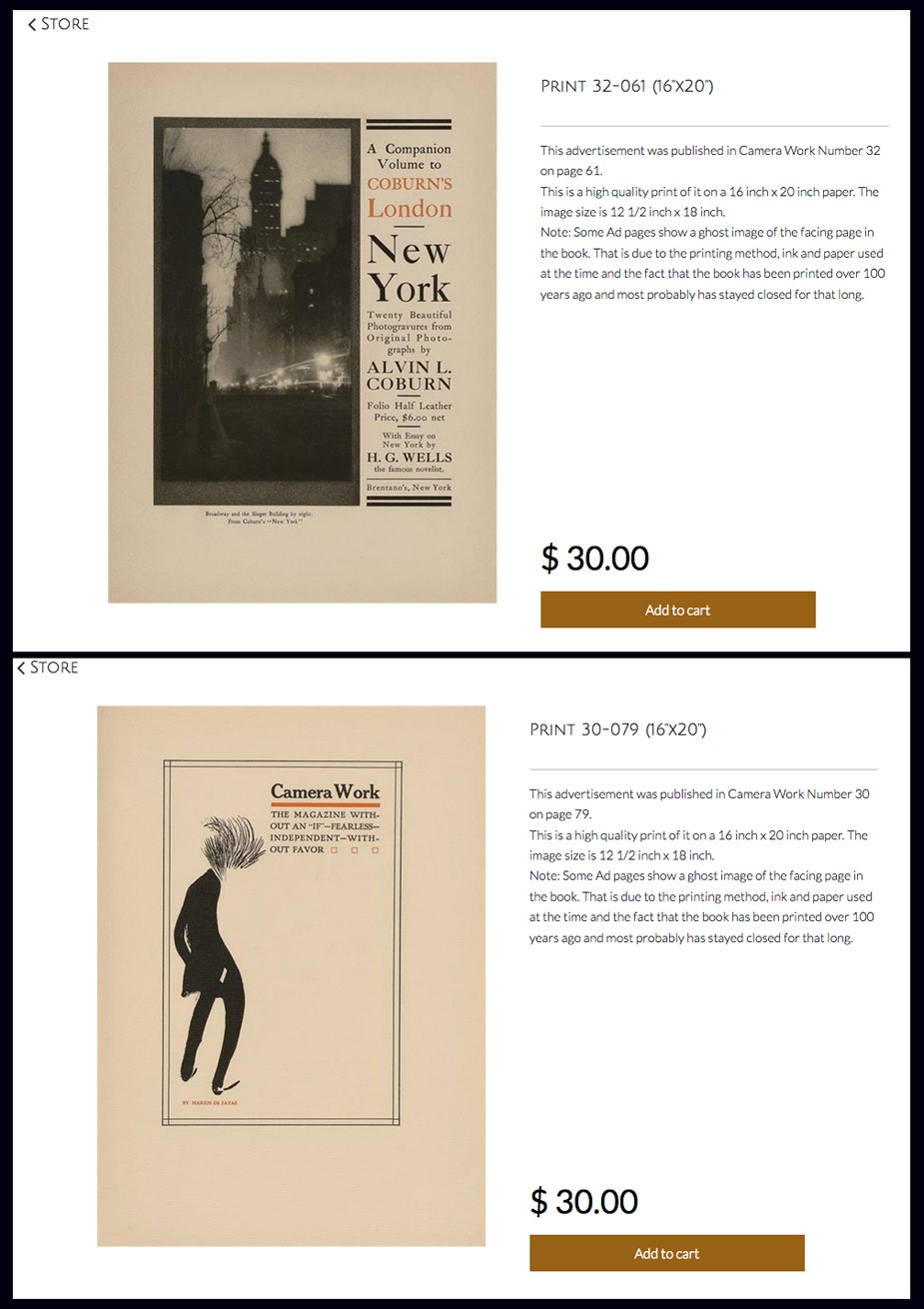
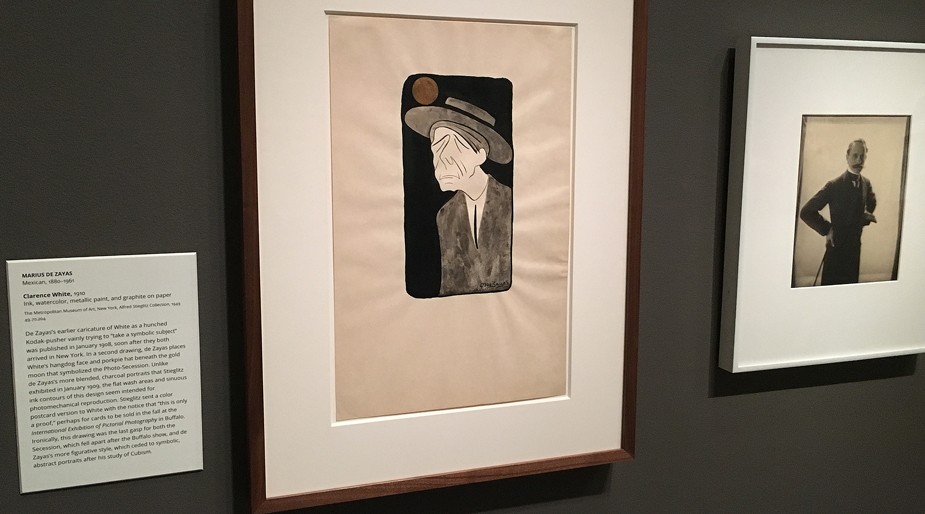
Ready for Framing: In addition to the full run of Camera Work along with a separate index issue, Pierre Vreyen’s website cameraworkmagazine.com features approximately 180 individual advertising pages from the journal that can be ordered as 16 x 20″ framable art prints for $30 each. At top, a vintage advertisement from Camera Work XXXII featured an actual photogravure from Alvin Langdon Coburn’s volume New York. At bottom, an ad shows a full-length caricature of Alfred Stieglitz by the artist Marius De Zayas featured in Camera Work XXX. Courtesy: Pierre Vreyen
1973: Friedman continues with the journal’s literature survey:
“Jonathan Green’s Camera Work: A Critical Anthology (1973) is the first significant evaluation of Camera Work, particularly focusing on the articles and text rather than the reproductions. It describes the evolution of the photographic medium through the writing in Camera Work from issue to issue over the fifteen years of its publication. The volume is thoroughly organized with six indexes: biographical information each of the artists, photographers, and writers who contributed to Camera Work and that are featured in his text; a chronological bibliography of works relating to Camera Work and the Photo-Secession; an index of names and subjects appearing in Camera Work; a chronological list of articles published in Camera Work; an index of artists and the issues in which their works appear; and a chronological index of the plates, listing the process by which they were reproduced in Camera Work.”
1973: Scholar Christian Peterson notes the following title which featured a facsimile of the Camera Work cover logo and publishing attribution for Stieglitz in his online sales catalogue for the journal:
Camera Work: A Photographic Quarterly Edited and Published by Alfred Stieglitz, New York, Minneapolis Institute of Arts, 1973. Softcover, 11 x 8 ½ inches, 40 pages, 3 halftone illustrations. This uncommon publication accompanied the exhibition, “I Am an American,” that traveled to over a dozen Minnesota towns in 1973 on the Minneapolis Institute of Arts’ Artmobile. The show included photogravures from Camera Work, plus paintings, drawing, and watercolors by members of the Stieglitz circle. This item includes a facsimile cover of the magazine, brief text by curator Carroll T. Hartwell, and reprints of articles from Camera Work. Most importantly, it features images by James Craig Annan, Alvin Langdon Coburn, and Stieglitz, printed on translucent paper and tipped-in, in a modest effort to replicate the delicate nature of the original gravures. Fine condition. $25. (editor: note: the “gravures” are actually halftones)
1978: Friedman continues with her thesis survey:
“In 1978 Marianne Fulton Margolis published Camera Work: A Pictorial Guide, building upon the thorough indexing in Green’s publication, but instead focusing solely on the images in Camera Work. This was the first time all 559 images from Camera Work were published in a single-volume reference. The images leave much to be desired; all are printed the same size, four to a page, in black and white halftone. As a reference, though, the publication is invaluable. The main part of the book reproduces each image in Camera Work in their exact sequence as published. Like Green, Margolis lists the medium by which the image was reproduced in Camera Work, but she also provides the original medium of the work when known, and also indicates when the reproduction is known to have been created from the artist’s original negative. Further, Margolis provides the reproduction method for every illustration in each issue of Camera Work, whereas Green discussed the plates, and a number of graphics within the text (such as Steichen’s Photo-Secession poster in Camera Work Number 13) which Margolis has not included in her index. Much of this information comes directly from the text of Camera Work. Three additional indexes at the end of the book provide an alphabetical list of artists, titles and portrait sitters, each with corresponding number of the periodical.”
1985: Friedman survey continues:
“This same concern was raised again in 1985 in the exhibition Camera Work: Process and Image organized by the Minneapolis Institute of Arts and accompanied by a catalogue with an essay by Christian A. Peterson that chronicles the use of reproductions throughout the publication of Camera Work, and the response these images provoked in the photographers whose works were reproduced.”
1997: Camera Work- The Complete Illustrations 1903-1917 is published by Benedikt Taschen with an essay in English by Pam Roberts that was additionally translated into German and French for the volume. Along with a full index of all artists represented in the journal and selected texts printed in the rear of the volume, all of the plates are reproduced which were taken from a complete set of Camera Work owned by the Royal Photographic Society, Bath.
Roberts notes in her essay: “Camera Work fulfilled many functions. On one level, it began as the last outpost of the confluence of Symbolist art, photography and literature, and ended as a messenger of Modernism. On another level, it was a non-concurrent exhibition catalogue for 291 and the publicity machine for the Photo-Secession.”

Pierre wears a Blue Shirt: Each issue of the full run of the newly re-issued Camera Work magazine plus a new separate index issue published in May, 2018 is featured in short video clips from back to front by Pierre Vreyen at his website cameraworkmagazine.com. At top, “The Steerage” by Alfred Stieglitz in Camera Work XXXVI. Courtesy Pierre Vreyen
Friedman’s thesis also comments on the 15th anniversary edition of this work: “An alternate version of this book, Camera Work: The Complete Photographs, published in 2008 for the l5th anniversary of Taschen, features reproductions of every photograph in Camera Work, but not every illustration as its predecessor does.”
2003: “Camera Work: A Centennial Celebration” is published. Friedman comments:
“In celebration of the 100th anniversary of the publication of Camera Work, a traveling exhibition was organized by Stephen Perloff, editor of The Photo Review and The Photograph Collector. A double issue of The Photo Review was published as a catalogue and featured essays by Perloff along with Peter C. Bunnell, Lucy Bowdich, Barbara L. Michaels, and Luis Nadeau.” (33.)
33. Perloff, Stephen, ed. “Camera Work: A Centennial Celebration.” Exhibition catalogue. The Photo Review 26, no. 1-2, 2003.
Camera Work Resources & Scholarship on the Web
– Wikipedia: always a good resource if you are just getting your feet wet in first learning about Camera Work. Link
– Modernist Journal Project: originally founded at Brown University in 1995 to create an online periodicals database, the entire run of Camera Work, using vintage copies from Princeton University, has been digitized in the last five years and posted online. Brown teamed with The University of Tulsa for the effort, which lacks only six photographic plates-Gertrude Käsebier’s “Portrait (Miss N)” and “Red Man” (CW 1: 11, 13), A. Radclyffe Dugmore’s “Study in Natural History” (CW 1: 55), Eduard Steichen’s “Solitude” and “Poster Lady” (CW 14s: 33, 35), and Steichen’s “The Photographer’s Best Model: G. Bernard Shaw” (CW 42-43: 39). Link
– Photogravure.com: Site owner and collector Mark Katzman has made all of the gorgeous photogravure plates (as well as most of the halftone plates) throughout the entire run of Camera Work accessible from his personal collection in the newly relaunched version of his site. Link
– Heidelberg University Library in conjunction with The University of Zurich launches their digitization efforts to the web in March, 2018: “all fifty regular and three special issues of Camera Work are digitized to the highest standards“. Link
– Camera Work: Inside/Out: Under the guidance of Professor Dr. Bettina Gockel, the principal investigator for the project, the University of Zurich from 2015-18 launches this research project in conjunction with the Institute of Art History at the university. Link
– Video: Camera Work – Institute of Art History University of Zurich: With a running length of about 5.5 minutes, this video produced as part of “Camera Work: Inside/Out” is a wonderful tribute to the enduring legacy and importance of the journal, and a fitting end to our post. Link
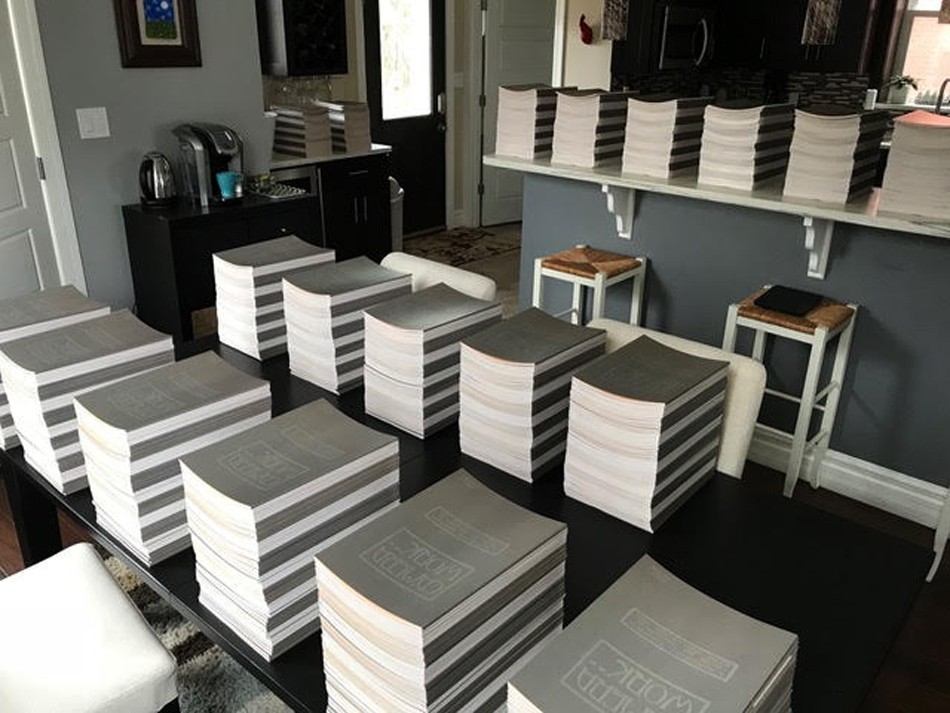

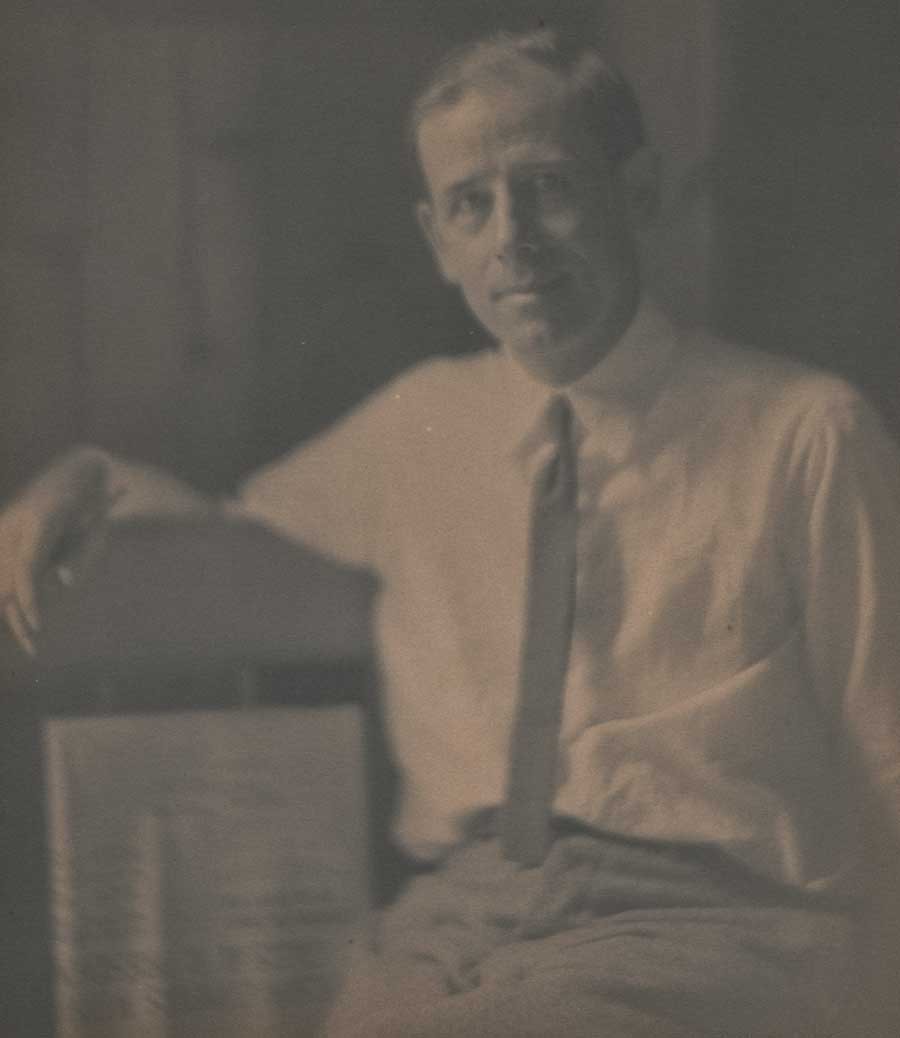
Editor, Publisher & Shipper: As seen here, St. Louis, MO resident Pierre Vreyen told PhotoSeed: “I picked up 25 sets of Camera Work from the printer yesterday. 1275 books!!! That’s a lot of books spread around my house. I am currently stacking them all in sets…” Well done, Pierre and good luck on your new endeavor I say! Courtesy Pierre Vreyen
Notes:
1. Letter excerpt: in auction listing by RR Auction, Amherst, NH April, 2018-lot passed- #0537. Additionally, the first two sentences of this letter cited in footnote #15 by Lori Cole for her essay “Camera Work: Forming Avant-Garde New York” published in the 2013 volume The Aesthetics of Matter: Modernism, the Avant-Garde and Material Exchange with cited source being the Alfred Stieglitz/Georgia O’Keeffe Archive at Yale University’s Beinecke Rare Book Library. (p. 186) (Note: the 2008 volume edited by Robert Wojtowicz titled Mumford on Modern Art in the 1930s states carbon copies of letters, believed to include this one sent by Stieglitz to Mumford, are contained within the Alfred Stieglitz correspondence files at the Beinecke.) The actual bonfire set by Stieglitz is corroborated somewhat in a description by Sue Davidson Lowe, the grandniece of Stieglitz, who writes in her volume: Stieglitz-A Memoir/Biography (1983) that in 1929, when Stieglitz was at Lake George and experiencing an emotional helplessness because he had not heard from Georgia O’Keeffe for several weeks, took to the cathartic act of burning: “an accumulation of papers-books and pamphlets, magazines (including many issues of Camera Work), negatives, and prints.” p. 294
2. ALS signed “Stieglitz,” three pages on two sheets, October 15, 1935, in part. (Stieglitz to Lewis Mumford) From auction listing: RR Auction, Amherst, NH April, 2018-lot passed- #0537.
3. ‘CAMERA WORK: A PHOTOGRAPHIC QUARTERLY’ Alfred Stieglitz, Editor: Sotheby’s: 03 OCTOBER 2012: Lot 55